Radon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas. It occurs naturally in minute quantities as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains through which thorium and uranium slowly decay into lead and various other short-lived radioactive elements. 195 Rn, 196 Rn, 197 Rn. Atomic Mass: Atomic mass number given for longest lived isotope. Density: Density at 0° Celsius. Specific Heat: Value given for gas phase.
- 47 sentence examples: 1. Xenon Chemical element, chemical symbol Xe, atomic number 54. Radon: Chemical element, chemical symbol Rn, atomic number 86. The atomic number appears as a subscript. Lead (atomic number 82) and gold (atomic number 7.
- Atomic Number of Elements in Periodic Table. We remember from our school chemistry course that every element has its own specific atomic number. It is the same as the number of protons that the atom of each element has, so sometimes atomic number is called proton number. It is always the whole number and it ranges from 1 to 118, according to.
| Atomic Structure | |
|---|---|
| Symbol | Rn |
| Atomic Number | 86 |
| Atomic Mass | 222 g/mol |
| Periodic Table | |
| Group | 18 |
| Row / Period | 6 |
| Element Category | Nonmetal, Noble gas |
| Chhapa | |
Radon ke electron shell | |
Radon ek chemical element hae jiske symbol Rn, atomic number 86, aur atomic mass 222 hae.
| Periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn | ||||||||||
| Fr | Ra | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Atomic Number Of Rn
Radon is a radioactive gas that forms naturally when uranium, thorium, or radium, which are radioactive metals break down in rocks, soil and groundwater. People can be exposed to radon primarily from breathing radon in air that comes through cracks and gaps in buildings and homes. Because radon comes naturally from the earth, people are always exposed to it.
See also:
Rn Atomic Number Definition
Rn Atomic Number Table
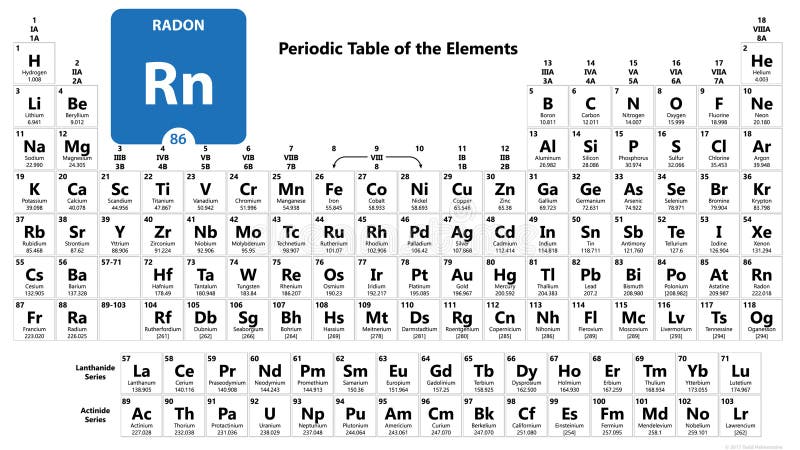
- Radiation Protection Division: Radon - https://www.epa.gov/radiation/radionuclide-basics-radon
- EPA's Integrated Risk Information System profile on Radon 222 [CASRN 14859-67-7] is located at: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/subst/0275_summary.pdf
Read more about Radon at www.epa.gov/radon





